|
gm. Elbląg, pow. elbląski, woj. warmińsko - mazurskie
Until 1945 Fischerkampe TK (, Schrőtter), Fischer Wohnungen (Endersch)
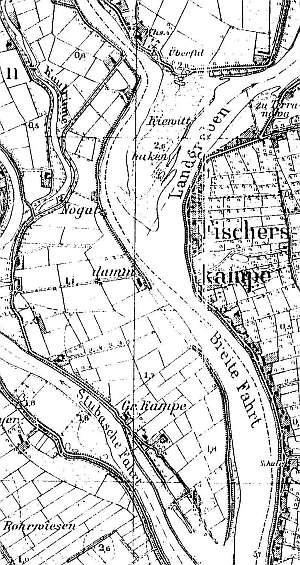
The village was included in the Elbląg territory. The first attempt (mid 1600s) to settle the Dutch colonists was unsuccesful. In 1683, the area was leased to Otto Ulbitz and then to Ernest Fisher. The village was re-founded in 1691. In 1715, it had 8 włókas and 21.5 morgas. The village was destroyed by 1763 and 1764 floods. In 1820, the village was inhabited by 272 residents, including 69 Mennonites. In 1919, it had 358 ha of land and 322 residents. Village layout - flood bank row village on the eastern bank of the Cieplicówka Canal. The cultural landscape (spatial layout with homesteads and field system) and historical buildings are in decline. In the 1980s, surveyors identified 30 historical buildings. Currently, there are 10 Dutch homesteads of the longitudinal type and 1 of the angular type, but they either include modern buildings or the historical buildings have been so heavily modified that their character is unrecognizable. Basically, only one longitudinal homestead with a wooden building has survived. It is a detached wooden house dating from the beginning of the 20th century. Several masonry houses from the beginning of the 20th century also have survived. Remains of an old lock are still present at the outlet of the Jagielloński Canal. Now, there is a bridge above them.
 No. 23 is a Dutch homestead of the longitudinal type situated
on the eastern side of the flood bank, facing the road with its ridge (a
home on southern side). The farming buildings are slightly higer and are
separated from the residential section by a high fire wall. The house
dates from the 4th quarter of the 19th century. It has a brick foundation,
a log structure with quoins covered by boards imitating Tuscan pilaster, a
half-timbered pointing sill, a vertically boarded gable, a wooden, queen
post - purlin roof structure, and pantile roofing. The gable elevation has
2 axes. The western (frontal) elevation has 6 axes at the ground floor and
an entrance between semicircular windows in the 3rd axis from the north.
The pointing sill is equipped with 3 rhomboidal skylights. No. 23 is a Dutch homestead of the longitudinal type situated
on the eastern side of the flood bank, facing the road with its ridge (a
home on southern side). The farming buildings are slightly higer and are
separated from the residential section by a high fire wall. The house
dates from the 4th quarter of the 19th century. It has a brick foundation,
a log structure with quoins covered by boards imitating Tuscan pilaster, a
half-timbered pointing sill, a vertically boarded gable, a wooden, queen
post - purlin roof structure, and pantile roofing. The gable elevation has
2 axes. The western (frontal) elevation has 6 axes at the ground floor and
an entrance between semicircular windows in the 3rd axis from the north.
The pointing sill is equipped with 3 rhomboidal skylights.
Kerstan, s. 209 -211; ML, t. I, s. 548 - 550; Piątkowski, Lipińska, t. III, poz. 64; AG.
|

 No. 23 is a Dutch homestead of the longitudinal type situated
on the eastern side of the flood bank, facing the road with its ridge (a
home on southern side). The farming buildings are slightly higer and are
separated from the residential section by a high fire wall. The house
dates from the 4th quarter of the 19th century. It has a brick foundation,
a log structure with quoins covered by boards imitating Tuscan pilaster, a
half-timbered pointing sill, a vertically boarded gable, a wooden, queen
post - purlin roof structure, and pantile roofing. The gable elevation has
2 axes. The western (frontal) elevation has 6 axes at the ground floor and
an entrance between semicircular windows in the 3rd axis from the north.
The pointing sill is equipped with 3 rhomboidal skylights.
No. 23 is a Dutch homestead of the longitudinal type situated
on the eastern side of the flood bank, facing the road with its ridge (a
home on southern side). The farming buildings are slightly higer and are
separated from the residential section by a high fire wall. The house
dates from the 4th quarter of the 19th century. It has a brick foundation,
a log structure with quoins covered by boards imitating Tuscan pilaster, a
half-timbered pointing sill, a vertically boarded gable, a wooden, queen
post - purlin roof structure, and pantile roofing. The gable elevation has
2 axes. The western (frontal) elevation has 6 axes at the ground floor and
an entrance between semicircular windows in the 3rd axis from the north.
The pointing sill is equipped with 3 rhomboidal skylights.